Osteochondria is one of the most common pathologies of the spine.In this disease, the tissue of the cartilage of the spine and the intervertebral discs are affected.Most of the time, osteochondria affects the lumbar region, as it is in this maximum load during walking, living room, running and other activities.
If treatment does not start in time, then the disease can lead to radical, intervertebral hernia, lumbar, ishias, disability.
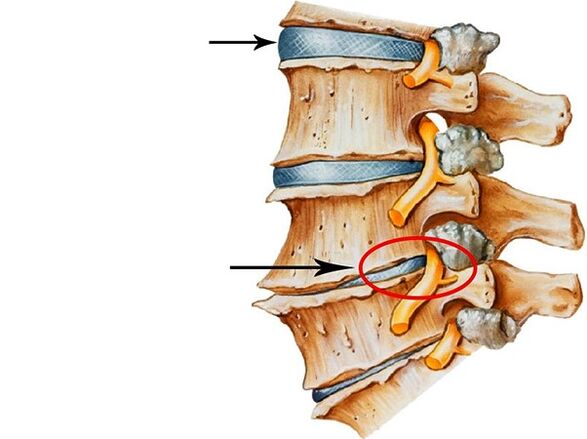
Stages of growth
The disease is usually divided into several stages:
- Stage 1st- There are minor changes to the intervertebral discs, the spine is not deformed, a person feels slight pain in the lower back.
- Stage 2- Pain in the affected area becomes stronger, violations of intervertebral discs become more noticeable.
- Stage 3- There are intervertebral hernias, the spine is deformed.The patient feels severe pain in the affected area.
- 4th stage- It becomes difficult for a person to walk and make any moves.Pain occurs with little movement.At this stage, the latter, the patient receives a disability, as a rule.
Causes
Most of the time, people whose profession or type of activity are associated with physical exercise and high loads in the lumbar part: builders, mobile, utility workers and athletes are subject to osteochondria.Also, the pathology can happen to teachers, cashiers, office employees, as they spend most of the time in a sitting position.
There are many factors that affect the appearance of osteochondicity:
- Lack of physical activity, conducting a sedentary lifestyle.
- Strong load in the lumbar region.
- Diseases of the joints and spine.
- Injuries to the lumbar spine.
- Flat legs or clubfoot.
- Portliness.
- Poster disorders, shade.
- Scoliosis or kyphosis.
- Long -term hypothermia.
- Age -related changes in the spine.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Some internal diseases of cardiovascular, nerve, endocrine systems.
- Inappropriate nutrition.
Symptoms
The main signs of osteochondrying of the lower back are:
- Powerful pain in the lower back, sometimes giving up on the leg and intensifying in the performance of any movement, sneezing, coughing, etc.
- Stable tension of the rear muscles.
- The inability to straighten the back after a long stay in the same position.
- Unpleasant sensations when tilting or back expansion.
- Lights on the lower back.
- Loss of sensitivity to buttocks, hips.
- Goosebumps, a feeling of tingling on the legs.
- Numbness of legs and feet.
- The constant coolness of the legs and the feeling of cold in the legs.
- Varicose veins.
- Violation of power in men.
- Irregular menstruation in women.
The main symptom of pathology is pain, when the appearance of which you should urgently consult a doctor.
Diagnosis
The diagnosis of osteochondry begins with a thorough examination of the patient and the collection of renewal - the doctor asks the patient to deal with cases of osteochondry in the genus, chronic diseases, lifestyle, type of activities, common illnesses and spine.
In addition, the expert defines organic methods of diagnostics, including:
- X -ray of lumbar region- It allows you to detect the presence of pathology and the degree of spine.
- Computed tomography (CT)- A more accurate method of research that allows you to determine the damage to the intervertebral discs, the degree of change, the degree of deformation of the spine.
- Magnetic resonance imaging- Allows you to study the interdisciplinary discs in detail, provides information on minor spine disorders, is used in difficult cases or if the examination of the examination using CT or x -ray examination is unclear.
- Myelography- A type of diagnosis in which a contrast factor is used for detecting intervertebral gardens.
Based on the data, the expert determines the degree of pathology and prescribes the necessary treatment.
Treatment
The treatment of osteochondry is performed overall.The necessary medicines and procedures are prescribed only by a doctor, strictly individually.
First of all, the patient has been prescribed by some drugs based on NSAIDs -not -Serreal anti -inflammatory drugs that can relieve inflammation and eliminate pain in the affected area.Chondrop Protectors are also prescription - drugs that stop the process of destruction of cartilage and cartilage supplies.Vitamins that improve the condition of the whole body are prescribed as additional medicines.
For many diseases of the spine, including osteochondicism, physiotherapy is prescribed.The procedures are able to enhance blood circulation in damage, relieve muscle tension, eliminate pain and inflammation.With osteochondria, electrophoresis, acupuncture, magnetic therapy and other procedures are prescribed.
The patient is also prescribed massage, mud baths or hydrotherapy that can relieve the tension and fatigue of the muscles, relax and enhance blood flow.Muddy mud baths can eliminate the inflammatory process.
In the early stages of the disease, exercise therapy is prescribed - a color gym, the performance of which helps to restore spine mobility to strengthen back muscles.In the 3 and 4 stages of osteochondrication, this type of treatment is not used.
Diet is very important for the treatment of the disease - it is necessary to include food products rich in minerals - fruits, vegetables, porridge.Be sure to eat low meats, as it is rich in protein - it will be very useful to eat chicken or turkey meat.It will be useful to use fermented dairy products.It is recommended to reduce the amount of fat, sharp, smokers, fried dishes.It is important to observe alcohol consumption function - be sure to drink at least 1 liter of clean water per day.
With the lumbar osteochondria, treatment in a sanatorium will be useful, where experts during the entire patient's stay in the complex will treat the disease and the patient is constantly under the supervision of doctors.
If conservative treatment methods do not help, then the surgical method of treatment is used.During operation, affected wheels or cartilage are replaced by an implant.And if there is an intervertebral hernia, then it is removed.
Prevention
- Limit the load to the lower back.
- Play sports, do breakfast exercises.
- Eat correctly.
- Try to prevent injuries of the lumbar spine.
- Avoid hypothermia of the lower back.
- With a long seat, change the body position more often, pick up regularly and do simple exercises for hot -up or just walk.
- Save the correct posture, do not climb.
- In the case of clubfoot or flat legs, they wear special orthopedic pellets that reduce the load on the spine.

















































